 An acid is a substance that can deliver protons (H + ions). What remains is the negative acid residue. Acids are the counterparts of the bases. An aqueous acid solution is referred to as the pH (acidity on a scale of 0-14) is lower than 7. (p = Potenz, H: hydrogen ion H+)
An acid is a substance that can deliver protons (H + ions). What remains is the negative acid residue. Acids are the counterparts of the bases. An aqueous acid solution is referred to as the pH (acidity on a scale of 0-14) is lower than 7. (p = Potenz, H: hydrogen ion H+)
The acid value indicates the number of hydrogen ions in a concentration.
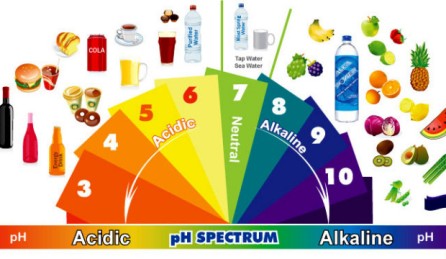
A concentration of 1 in 10 million = 1/107 = pH 7
A concentration of 1 in 1 million = 1/106 = pH 6
Citric acid and acetic acid are known materials which impart a sour taste. In high concentrations, if the pH is lower than 1 acids may be harmful. A pH lower than 4.5 is toxic to multiple (water) animals. A pH lower than 1.5 could cause burns (skin dissolve).
pH 14: sodium hydroxide solution of 1 mol / l
pH 13: sodium hydroxide solution or potassium hydroxide solution 0,1 mol / l
pH 12: oven cleaner
pH 11.5: household ammonia (ammonia solution so)
pH 10.5: soapsuds
pH 9.5: bleach
pH 8.5: seawater, intestinal fluid (pH slightly increased by bile)
pH 7.5: eggs
pH 7.4: human blood
pH 7: pure, distilled water (neutral), and dune sand clay soil
pH 6.7: milk
pH 6.5: saliva
pH 6: natural rain, urine, sandy soils
pH 5.5: Skin
pH 5: slightly acidic rain, peat
pH 4.5: tomatoes, grapes
pH 4: acid rain, tomato juice, beer
pH 3.5: apple, orange juice
pH 3: consumption vinegar, wine, sauerkraut, currant
pH 2.8: cola, vinegar
2 pH: stomach acid, lemon juice
pH 1: sulfuric acid (battery acid)
pH 0: hydrochloric acid (1 mol / l), sulfuric acid (1 N)
Base metals such as iron, zinc and magnesium dissolve in acids (e.g. hydrochloric acid) while releasing hydrogen gas.
In concentrated sulfuric acid, nitric acid or aqua regia also noble metals dissolve, because they are strong oxidizers.
A base in solution has a pH - value higher than 7, and will color litmus paper blue.
Acids are neutralized by bases to form a salt and water. Weak bases, such as aluminum hydroxide, can be used to temporarily neutralize gastric acid. Strong bases are as dangerous or more dangerous than strong acids and cause severe tissue damage. An example of a strong base is sodium hydroxide.
The acidity determines (the viability of) the soil life, and the binding and thus the availability of minerals for soil and plants.
Anthocyanin, the red substance in red fruits and red cabbage for example, was used as an acid / base indicator. Many natural dyes also fade as the pH changes. Anthocyanin is pinkish- red in an acidic environment, and blue, green and yellow in an alkaline.
If you add to a fabric an acidic solution (such as hydrochloric acid or vinegar), the solution turns red. With an alkaline solution (such as sodium hydroxide or soda or ammonia) colors the fabric of blue and green, yellow. Therefore, one adds an apple in the preparation of red cabbage, by the acid, it is given a red cabbage a more comfortable, lighter color.
Litmus paper is made of litmus, a vegetable dye that is extracted from lichens, mainly from Lecanora tartarea and Rocella tinctoria. It turns red when it comes into contact with acids, and blue when it comes into contact with a base. In a neutral environment it's purple.
|
Table: Reactions with acids and bases of plant substances |
||||
|
commodity |
color |
color extract |
+ acid |
+ base |
|
dewberry (Rubus caesius |
blue |
red |
red |
blue -green |
|
blackberry (Rubus fruticosus) |
black |
red |
red |
blue -green |
|
currant (red berry) |
red |
red |
red |
blue -green |
|
strawberry |
red |
orange |
orange |
deep red |
|
rose tree flower |
red |
pink |
deep red |
groen-bruin |
|
chrysanthemum flower |
yellow |
pale yellow |
yellow |
|
|
rose |
orange |
yellow |
orange |
brown |
|
dubia (flower) |
purple |
weak pink weak pink |
violet |
fresh greenfresh green |
|
fuchsia flower |
red |
colorless |
violet |
brown |
|
beet |
red |
red |
violet |
light |
|
red cabbage |
purple / white |
violet |
deep red |
fresh green |
Self-pity is the acid that eats holes in happiness. (Earl Nightingale)
Men are like wine. Some are sour, but most get better as they get older.
