Nuclear fission is used to make huge amounts of energy. We use that energy through nuclear power plants for electricity or nuclear bombs and as an energy source for nuclear submarines.
 As fuel (enriched) uranium (and plutonium) are used. An atom is shot, causing splashing neutrons and electrons, which can also hit nuclei and split again, etc.
As fuel (enriched) uranium (and plutonium) are used. An atom is shot, causing splashing neutrons and electrons, which can also hit nuclei and split again, etc.
Concentrated, this leads to a nuclear explosion,
under control it produces much heat that is used in nuclear power plants to drive turbines and make electricity.
The reaction yields altered nuclei with more or less protons and / or neutrons. This chang(ing) atoms are radioactive: they emit ionizing rays: energy that can ejected electrons from an atom.
Our civilization is not yet a hundred thousant years. The decay of dangerous radioactive material into harmless substance takes hundreds of thousands of years. Storage is also a problem for future generations.
A high radiation has serious consequences: malformations in the offspring, cancer or even sudden death.
By radiation DNA molecules may be damaged, and cells transformed or slain. Uncontrolled cell division is leading to cancer and genetic mutations that accumulate over several generations. Chances of this increase with the degree of exposure, intensity, quantity, type of radiation, duration.
The mutilated elements (atoms) will in (sometimes very long) term evolve back to a stable state. But meanwhile they are and remain active for years and centuries.
Radioactive pollution is invisible. Everything that comes into contact with it is infected: tools, fluid, full- power stations, mines, tailings,... That makes cleanup priceless.
The United States have three nuclear bombs detonated in 1945: a test in the New Mexico desert, then followed the destruction of the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
More, and more powerful bombs were made and tested also by the Soviet Union and other countries, where in addition the first are small fry.
A treaty between the U.S. and the Soviet Union banned aboveground nuclear tests since 1963.
Meanwhile, we count 543 overhead + 1876 underground = 2419 trials (the number of bombs is even higher), with a land share: 1054 U.S. 715 SU, France 210, GB 45, China 45, India 7, Pakistan 6, North Korea 1, Israel and South Africa 1 (2012).
After the arms race between the U.S. and SU was in 1998 in Asia also one between India and Pakistan.
India, Pakistan and Israel have not signed the Nuclear Non- Proliferation Treaty (against the spread of nuclear weapons), North Korea has denounced in 2003.
There are about 35,000 nuclear weapons in the world. The U.S. has 5,300 operational warheads and 5,000 in the 'responsive reserve force'. Russia 7,200 operational warheads, China 400, France 350, UK 200, to 400 Israel, Pakistan to 50 and India 30 to 35. North Korea?
Fallout, radioactive or nuclear precipitation is the radiation hazard of falling down dust after a nuclear explosion in the atmosphere or on the surface. Not only the material of the bomb itself is radioactive, dust that swirls up by intense neutron irradiation of the explosion also is radioactive by neutron capture.
A “Nuclear Winter“ is caused by the millions of tonnes of carbon into the atmosphere as a result of all fires caused by multiple nuclear explosions. This cloud block the sunlight, with global crop failures and famine in humans and livestock as a result.
Even if nuclear weapons are never used have manufacturing, testing, and saving a huge environmental impact.
Nuclear power plants are mainly in industrialized regions: U.S., USSR, Europe and Japan. The world counts are 442, of which 197 in Europe. According to the IAEA is around 20 percent in areas with "significant seismic activity.“ This additional risk is particularly in Japan and Taiwan, but also India, Turkey and Chile join it.
A meltdown is an accident in a nuclear reactor in which the core of the reactor gets overheated and fuel elements melt. This may result in radioactive material that is released, and in any case the reactor is unusable until the core is repaired or replaced. In a very serious scenario, the nuclear chain reaction could get out of hand and the reactor mass melts through the bottom of the reactor vessel and the reactor building in the ground (China Syndrome). In cases where a (partial) meltdown occurred, this was not the case.
The first blast in September 1957 (Kyshtym, Urals) has long been kept quiet by the Russians.
The hasty construction of the original central Windscale (now Sellafield - Great Britain) has led to many accidents. For example:
on October 9, 1957 there was a fire in the reactor vessel,
on April 18, 2005 it was discovered that for nine months a break in a pipeline had gone unnoticed!
In the Mayak reprocessing plant in Russia have been two major and several minor nuclear accidents in the 50s and 60s of the last century.
On March 28, 1979 there was a meltdown at Three Mile Island nuclear plant in Harrisburg, United States with lots of radioactive gas into the atmosphere. Only after six years, the reactor could be opened. Then it appeared that the injury was more serious than initially believed. And only in 1993 the cleaning of the reactor vessel was largely completed.
Chernobyl, 25-26 April 1986: after an error in a test the reactor was inadvertently almost completely shut down.
Through a combination of successive problems and errors temperature and power rose still further, and a steam explosion blew the 2,000 ton roof of the reactor off.
After ten days, approximately 135,000 people were evacuated from an area with a radius of 30 km around the reactor. This 'alienation zone' is still strictly forbidden area.
Around May 2 radioactive clouds reached the Netherlands and Belgium.
In the Netherlands, a grazing ban was imposed in order to prevent infection of milk. Fresh leafy vegetables should not be sold. In Belgium, no action was taken. Weatherman Armand Pien could not say how high the radiation from the radioactive cloud was. It was just 'shining' weather.
Especially the consumption of wildlife, deer, and wild mushrooms are absolutely to be avoided. Is today still said in Germany.
After the fire was extinguished reactor four was encased in a concrete sarcophagus, which was completed in November 1986. This shell is current (still / again) in irresponsible condition. The cost to foreclose the remnants of the plant are estimated at € 1.54 billion, money that Ukraine has not.
In 1995, Ukraine also asked $ 900 million on the G8 countries to permanently shut down the Chernobyl plant. That happened only in 2000.
The number of deaths from this disaster is between 4,000 and 200,000.
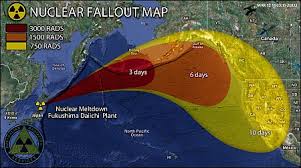
On March 11, 2011, the nuclear power plants in Fukushima in Japan proved insufficient to withstand natural disasters of a tsunami.
The next day, 170,000 people had to leave a radius of 20 km, after a month extended to 30 km.
The U.S. aircraft carrier USS Ronald Reagan at 160 km off the coast measured radiation.
On March 23, radioactive iodine was found in the drinking water of Tokyo (200 km) in an amount that is dangerous for children up to one year. Also in vegetables and milk from the area elevated levels of radioactive iodine and cesium were found.
On May 11 in the grass in Marumori, 60 kilometers from Fukushima concentrations were found of elevated radioactive cesium that exceeded five times the maximum legal value.
At every nuclear disaster information always came piecemeal, incorrectly and much too late in an attempt to avoid panic and responsibility as much as possible.
Everyone is constantly exposed to background radiation: natural ionizing radiation from the cosmos (sun and stars), naturally occurring radioactive materials in rocks and soil, radionuclides normally found in the body tissues, and radon and its products that we breathe. To date, one cannot say what level of risk would be associated to it.
In nuclear disasters iodine tablets are to be swallowed in order to prevent the body to absorb the radioactive isotope thereof.
You can even monitor the radioactivity in your area through http://telerad.fgov.be/
La Hague in France and Sellafield on the northwest coast of the United Kingdom are reprocessing plants with high concentrations toxicants in the discharges, that can be found in the environment, water, shellfish...
Used reactor fuel can be recovered for reprocessing here, an environmentally unfriendly process in which a large amount of additional radioactive waste is created, with many accidents and irresponsible emissions of radioactive material.
In contrast to toxic chemical compounds, which in principle can be broken down into atoms, are radionuclides elements which are not destroyed, or may be made harmless in a chemical way.
A major concern is currently the secure storage and insulation. For thousands of years.
The residual 'depleted uranium' doesn’t occur in nature. It is a toxic heavy metal (1.7 times as heavy as lead) and is used in missiles and civilian applications. So get military and industry off of hazardous waste mainly through the battlefield. The fallout from depleted uranium dust penetrates everywhere. Many components come after use just on the junkyard!
Nuclear submarines (remain long under water)
To date, seven nuclear submarines sank, two from the U.S. and five of the Soviet Union. The first was the USS Thresher in 1963, then the USS Scorpion of the U.S. sank, and the K - 8, K- 429 (sank twice), K- 219, K -278 Komsomolets in the Norwegian Sea in 1989 and Kursk in the Barents Sea on August 12, 2000.
On and around the Kola Peninsula, northwest of the White Sea, are found many extremely dubious radioactive waste repositories. In various ports are 90 disused Russian nuclear submarines rusting.
In the Kara Sea, east of Novaya Zemlya, lay sixteen used nuclear reactors without containment. Also at nuclear power plants in the country are many and hazardous waste inventories. Leaks will already be...
If (disintegration) of a substance expires one atom per second , this substance is a radioactive source (radiation source) with a strength of 1 becquerel.
If food is more radioactive than 600 bequerels per kilogram, the government intervenes. The amount of natural radioactive substances in the human body is about 120 Bq / kg. The average person is a radioactive source of approximately 8,500 Bq.
To keep gamma rays for 95% are 6 centimeters of lead, 10 centimeters of iron or 33 cm of concrete needed.
Radioactivity is the broadcast of ionizing radiation. Certain isotopes are unstable and change (disintegrate) spontaneously in a different atomic species. This is called radioactive decay. Thus, there arise other nuclides, sometimes a different isotope of the same element, usually a different element. This process continues until a stable nucleus originates.
The half-life and the decay time show the time that an unstable and exponentially decaying particle requires to come to half of its activity or radiation. After that there is statistical, for a mass (not individually per atom) exactly one half of the quantity left.
For example tritium (3H), an unstable isotope of hydrogen. Tritium atoms can pass under appearance of an electron in helium. The half-life of tritium is 12.33 years. After 12.33 years, therefore, the half of the tritium is converted into helium. After an additional 12.33 years, there is only one quarter of the original tritium over, again after 12,33 year one eighth, etc.
Half-lives for some isotopes.
Iodine-131 8 days
Cesium -131 9.7 days
Cesium -134 2 years
Strontium -90 28 years
Cesium -137 30 years
Plutonium -239 24,400 years
Cesium -135 2.3 million year
Uranium - 235 704 million years
Uranium - 238 4.5 billion years
(More info: http://www.motherearth.org/nuke/milieu_nl.pdf)
We pollute our environment and the earth for millions, even billions of years with life-threatening mess. Who comes after us should just see what he does with it.
For 1000s of generations after us, the grandchildren will still have to bear care for our now already leaking barrels of radioactive waste...
More so than men, scientists are smart, but not wise.
The next war will be fought with nuclear bombs. The subsequent with spears. (Harold Urey)
Underground nuclear tests are like mushrooms: sooner or later they come to the table. (Bernard Seulsten)
Actual active: radioactive risk
Nuclear fission is used to make huge amounts of energy. We use that energy through nuclear power plants for electricity or nuclear bombs and as an energy source for nuclear submarines.
As fuel (enriched) uranium (and plutonium) are used. An atom is shot, causing splashing neutrons and electrons, which can also hit nuclei and split again, etc.
Concentrated, this leads to a nuclear explosion,
under control it produces much heat that is used in nuclear power plants to drive turbines and make electricity.
The reaction yields altered nuclei with more or less protons and / or neutrons. This chang(ing) atoms are radioactive: they emit ionizing rays: energy that can ejected electrons from an atom.
Our civilization is not yet a hundred thousant years. The decay of dangerous radioactive material into harmless substance takes hundreds of thousands of years. Storage is also a problem for future generations.
A high radiation has serious consequences: malformations in the offspring, cancer or even sudden death.
By radiation DNA molecules may be damaged, and cells transformed or slain. Uncontrolled cell division is leading to cancer and genetic mutations that accumulate over several generations. Chances of this increase with the degree of exposure, intensity, quantity, type of radiation, duration.
The mutilated elements (atoms) will in (sometimes very long) term evolve back to a stable state. But meanwhile they are and remain active for years and centuries.
Radioactive pollution is invisible. Everything that comes into contact with it is infected: tools, fluid, full- power stations, mines, tailings,... That makes cleanup priceless.
The United States have three nuclear bombs detonated in 1945: a test in the New Mexico desert, then followed the destruction of the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
More, and more powerful bombs were made and tested also by the Soviet Union and other countries, where in addition the first are small fry.
A treaty between the U.S. and the Soviet Union banned aboveground nuclear tests since 1963.
Meanwhile, we count 543 overhead + 1876 underground = 2419 trials (the number of bombs is even higher), with a land share: 1054 U.S. 715 SU, France 210, GB 45, China 45, India 7, Pakistan 6, North Korea 1, Israel and South Africa 1 (2012).
After the arms race between the U.S. and SU was in 1998 in Asia also one between India and Pakistan.
India, Pakistan and Israel have not signed the Nuclear Non- Proliferation Treaty (against the spread of nuclear weapons), North Korea has denounced in 2003.
There are about 35,000 nuclear weapons in the world. The U.S. has 5,300 operational warheads and 5,000 in the 'responsive reserve force'. Russia 7,200 operational warheads, China 400, France 350, UK 200, to 400 Israel, Pakistan to 50 and India 30 to 35. North Korea?
Fallout, radioactive or nuclear precipitation is the radiation hazard of falling down dust after a nuclear explosion in the atmosphere or on the surface. Not only the material of the bomb itself is radioactive, dust that swirls up by intense neutron irradiation of the explosion also is radioactive by neutron capture.
A “Nuclear Winter“ is caused by the millions of tonnes of carbon into the atmosphere as a result of all fires caused by multiple nuclear explosions. This cloud block the sunlight, with global crop failures and famine in humans and livestock as a result.
Even if nuclear weapons are never used have manufacturing, testing, and saving a huge environmental impact.
Nuclear power plants are mainly in industrialized regions: U.S., USSR, Europe and Japan. The world counts are 442, of which 197 in Europe. According to the IAEA is around 20 percent in areas with "significant seismic activity.“ This additional risk is particularly in Japan and Taiwan, but also India, Turkey and Chile join it.
A meltdown is an accident in a nuclear reactor in which the core of the reactor gets overheated and fuel elements melt. This may result in radioactive material that is released, and in any case the reactor is unusable until the core is repaired or replaced. In a very serious scenario, the nuclear chain reaction could get out of hand and the reactor mass melts through the bottom of the reactor vessel and the reactor building in the ground (China Syndrome). In cases where a (partial) meltdown occurred, this was not the case.
The first blast in September 1957 (Kyshtym, Urals) has long been kept quiet by the Russians.
The hasty construction of the original central Windscale (now Sellafield - Great Britain) has led to many accidents. For example:
on October 9, 1957 there was a fire in the reactor vessel,
on April 18, 2005 it was discovered that for nine months a break in a pipeline had gone unnoticed!
In the Mayak reprocessing plant in Russia have been two major and several minor nuclear accidents in the 50s and 60s of the last century.
On March 28, 1979 there was a meltdown at Three Mile Island nuclear plant in Harrisburg, United States with lots of radioactive gas into the atmosphere. Only after six years, the reactor could be opened. Then it appeared that the injury was more serious than initially believed. And only in 1993 the cleaning of the reactor vessel was largely completed.
Chernobyl, 25-26 April 1986: after an error in a test the reactor was inadvertently almost completely shut down.
Through a combination of successive problems and errors temperature and power rose still further, and a steam explosion blew the 2,000 ton roof of the reactor off.
After ten days, approximately 135,000 people were evacuated from an area with a radius of 30 km around the reactor. This 'alienation zone' is still strictly forbidden area.
Around May 2 radioactive clouds reached the Netherlands and Belgium.
In the Netherlands, a grazing ban was imposed in order to prevent infection of milk. Fresh leafy vegetables should not be sold. In Belgium, no action was taken. Weatherman Armand Pien could not say how high the radiation from the radioactive cloud was. It was just 'shining' weather.
Especially the consumption of wildlife, deer, and wild mushrooms are absolutely to be avoided. Is today still said in Germany.
After the fire was extinguished reactor four was encased in a concrete sarcophagus, which was completed in November 1986. This shell is current (still / again) in irresponsible condition. The cost to foreclose the remnants of the plant are estimated at € 1.54 billion, money that Ukraine has not.
In 1995, Ukraine also asked $ 900 million on the G8 countries to permanently shut down the Chernobyl plant. That happened only in 2000.
The number of deaths from this disaster is between 4,000 and 200,000.
On March 11, 2011, the nuclear power plants in Fukushima in Japan proved insufficient to withstand natural disasters of a tsunami.
The next day, 170,000 people had to leave a radius of 20 km, after a month extended to 30 km.
The U.S. aircraft carrier USS Ronald Reagan at 160 km off the coast measured radiation.
On March 23, radioactive iodine was found in the drinking water of Tokyo (200 km) in an amount that is dangerous for children up to one year. Also in vegetables and milk from the area elevated levels of radioactive iodine and cesium were found.
On May 11 in the grass in Marumori, 60 kilometers from Fukushima concentrations were found of elevated radioactive cesium that exceeded five times the maximum legal value.
At every nuclear disaster information always came piecemeal, incorrectly and much too late in an attempt to avoid panic and responsibility as much as possible.
Everyone is constantly exposed to background radiation: natural ionizing radiation from the cosmos (sun and stars), naturally occurring radioactive materials in rocks and soil, radionuclides normally found in the body tissues, and radon and its products that we breathe. To date, one cannot say what level of risk would be associated to it.
In nuclear disasters iodine tablets are to be swallowed in order to prevent the body to absorb the radioactive isotope thereof.
You can even monitor the radioactivity in your area through http://telerad.fgov.be/
La Hague in France and Sellafield on the northwest coast of the United Kingdom are reprocessing plants with high concentrations toxicants in the discharges, that can be found in the environment, water, shellfish...
Used reactor fuel can be recovered for reprocessing here, an environmentally unfriendly process in which a large amount of additional radioactive waste is created, with many accidents and irresponsible emissions of radioactive material.
In contrast to toxic chemical compounds, which in principle can be broken down into atoms, are radionuclides elements which are not destroyed, or may be made harmless in a chemical way.
A major concern is currently the secure storage and insulation. For thousands of years.
The residual 'depleted uranium' doesn’t occur in nature. It is a toxic heavy metal (1.7 times as heavy as lead) and is used in missiles and civilian applications. So get military and industry off of hazardous waste mainly through the battlefield. The fallout from depleted uranium dust penetrates everywhere. Many components come after use just on the junkyard!
Nuclear submarines (remain long under water)
To date, seven nuclear submarines sank, two from the U.S. and five of the Soviet Union. The first was the USS Thresher in 1963, then the USS Scorpion of the U.S. sank, and the K - 8, K- 429 (sank twice), K- 219, K -278 Komsomolets in the Norwegian Sea in 1989 and Kursk in the Barents Sea on August 12, 2000.
On and around the Kola Peninsula, northwest of the White Sea, are found many extremely dubious radioactive waste repositories. In various ports are 90 disused Russian nuclear submarines rusting.
In the Kara Sea, east of Novaya Zemlya, lay sixteen used nuclear reactors without containment. Also at nuclear power plants in the country are many and hazardous waste inventories. Leaks will already be...
If (disintegration) of a substance expires one atom per second , this substance is a radioactive source (radiation source) with a strength of 1 becquerel.
If food is more radioactive than 600 bequerels per kilogram, the government intervenes. The amount of natural radioactive substances in the human body is about 120 Bq / kg. The average person is a radioactive source of approximately 8,500 Bq.
To keep gamma rays for 95% are 6 centimeters of lead, 10 centimeters of iron or 33 cm of concrete needed.
Radioactivity is the broadcast of ionizing radiation. Certain isotopes are unstable and change (disintegrate) spontaneously in a different atomic species. This is called radioactive decay. Thus, there arise other nuclides, sometimes a different isotope of the same element, usually a different element. This process continues until a stable nucleus originates.
The half-life and the decay time show the time that an unstable and exponentially decaying particle requires to come to half of its activity or radiation. After that there is statistical, for a mass (not individually per atom) exactly one half of the quantity left.
For example tritium (3H), an unstable isotope of hydrogen. Tritium atoms can pass under appearance of an electron in helium. The half-life of tritium is 12.33 years. After 12.33 years, therefore, the half of the tritium is converted into helium. After an additional 12.33 years, there is only one quarter of the original tritium over, again after 12,33 year one eighth, etc.
Half-lives for some isotopes.
Iodine-131 8 days
Cesium -131 9.7 days
Cesium -134 2 years
Strontium -90 28 years
Cesium -137 30 years
Plutonium -239 24,400 years
Cesium -135 2.3 million year
Uranium - 235 704 million years
Uranium - 238 4.5 billion years
(More info: http://www.motherearth.org/nuke/milieu_nl.pdf)
We pollute our environment and the earth for millions, even billions of years with life-threatening mess. Who comes after us should just see what he does with it.
For 1000s of generations after us, the grandchildren will still have to bear care for our now already leaking barrels of radioactive waste...
More so than men, scientists are smart, but not wise.
The next war will be fought with nuclear bombs. The subsequent with spears. (Harold Urey)
Underground nuclear tests are like mushrooms: sooner or later they come to the table. (Bernard Seulsten)
